IDENTIFYING AND
PRIORITIZING FACTORS AFFECTING THE CUSTOMERS' WILLINGNESS TO BUY GOODS PRODUCT
INSIDE THAN ON THE OUTSIDE (CASE STUDY:
IRAN TRANSFO CORPORATION)
Haleh Keshavarz Afshar
Islamic Azad University of Medical Sciences, Iran, Islamic Republic of
E-mail: Haleh.k88@yahoo.com
Gholamreza Soleimani
Islamic Azad University of Medical Sciences, Iran, Islamic Republic of
E-mail: GH_Soleimani2006@yahoo.com
Submission: 26/01/2017
Accept: 01/03/2017
ABSTRACT
The present study aims to identify and prioritizing factors
affecting customers' willingness to purchase domestic goods than the foreign ones in Iran Transfo Corporation in 2016. The
statistical population includes all customers and a sample of 200 subjects (175
male, 25 female). Respondents' evaluation of the variables indicates that
Iranian goods enjoy market-product fit (0.85), good performance (0.41),
relative reputation and validity (0.44), high reliability (0.36), good
communication methods (0.34) and relative value (0.26). Finally, 88% prefer to
purchase Iranian goods. The effect of 7 independent variables and purchase
preferences are significant at (e < 0.05). The results of inferential
statistics show that there is a significant relationship between willingness to
purchase domestic and foreign goods. There is a significant difference between
marketing methods and satisfaction among
buyers of domestic and foreign goods as well. But, there is no significant difference between the
customers' evaluation of product features and performance of domestic producers
compared to the foreign ones. Finally, given that the majority of respondents
considered marketing methods inappropriate, therefore, it's recommended that
companies adopt new policies to better sell their products.
Keywords: Consumer Behavior,
Marketing Strategy, Purchase Preferences, Domestic and Foreign Goods, Iran Transfo Corporation
1. INTRODUCTION
World trade expansionist of utmost importance for the growth
and development of the
whole world economy. This
is important, in particular for countries that face a lack of resources. However, commercial
transactions (especially
imports) could sometimes leave negative outcomes within the countries.
When the domestic
industries (due to different reasons)are unable to compete with similar foreign
products or when
new methods of marketing for many products that are competitive with foreign
brands are ignored, imports impose a double pressure
on domestic production and customers are increasingly exposed to a wide range
of imported products (KNIGHT, 1999).
Several factors
in our country have made many industries unable to easily compete with similar
foreign products. Currently, foreign products in many cases have attracted
customers, and consumers' priority is to choose the foreign goods rather than
the domestic one. Here an important question is posed: What is the reason
behind consumers' willingness to buy foreign goods?
In response to
this question, some say it's the wrong culture that is prevailing the community
and some refer to the better quality of foreign products; both of these
theories have considered some reasons as the main cause. But the reality is
that consumers' willingness to consume foreign products in our country stems
from a series of factors, one of which is wrong culture of the society (consumer needs and
beliefs).
The
other is related to the malfunction of manufacturers, product specifications,
and poor performance of governmental organizations and the
weakness of rules and regulations and so on.
Attitudes, manner
and performance of manufacturer in producing and supplying the products are one of the main
reasons for the consumers'
willingness to buying or leaving the products. Manufacturers who focus their
activities purely on gaining profit in a short time period, cannot hope to
produce and sell their products (in the long-term), in contrast, manufacturers
who consider customer preferences and produce products tailored to their needs
and tastes (in terms of price, diversity, performance, standard, etc.) could be
a factor for further production and sale in the long term. International
standards and
products featuring
them are considered as an advantage.
Some foreign
products supplied in our country have the latest international standards which
also account for the consumers'
willingness to buy them. In contrast, some other similar domestic goods have
even failed to achieve the standards of our own country, such as the automobile
industry, etc (ELECTRONIC JOURNAL BHKAM, 2016).
These factors can
increase customer satisfaction and customer preferences. Customer satisfaction
is undoubtedly one of the strategic issues in recent decades occupying the
marketing managers' minds to provide a proper strategy to gain the trust of
customers to the domestic goods. Iran Transfo Corporation is not an exception, being the largest
manufacturer and exporter of transformers under license from Germany Siemens in
the Middle East.
Many factors
affect people's decisions to buy domestic products, attracting the attention of
scholars and researchers since many years ago. In 1950s, realizing the
customers and their needs was prioritized to raw materials and selling skills.
Freud's ideas were used by the marketers and researchers. Also in the 1960s,
consumer behavior became the main concern of studies, meaning that commercial
firms aimed at satisfying the demands and needs of consumers through
understanding the transaction parties.
Although
transaction is an important part of consumer behavior, but broader perspectives
today stress the whole consumption process involving factors affecting consumer
behavior before, during and after the purchase. Accordingly, internal and
external practical investigations have been carried out in this field and
purchase decisions; for example, the research results of Sadeghi et al. (2014) showed
that consumer shopping preferences include: quality, standard, diversity and
greater durability of foreign products, the sellers also state that increased
prices of raw material and consequently expensive domestic goods against cheap foreign
goods, and false culture
that implies foreign goods are better are among such factors (SADEGHI,
et al., 2014).
Heydarzadeh and Hasaniparsa (2013)
also found that hedonistic values have a positive effect on increasing novelty
seeking brand consciousness,
responsiveness to promotion stimuli, and preference for foreign brands (HEYDARZADEH;
HASANIPARSA, 2013). Mahmoudi
Meymand, et al. (2013) stated that personality types have a significant
difference in the attitudes of consumer towards involvement variables, knowledge and
willingness to purchase (MAHMOUDI MEYMAND et al., 2013).
The results of
Heidarzadeh et al. (2010) showed that customers studied have a different
assessment of the characteristics of goods, related marketing methods and
purchase preferences of the goods in two countries. By prioritizing factors
affecting the purchase preferences, companies operating in the market can use
them to optimize their marketing strategy (HEIDARZADEH, et al., 2010).
Haghighi and
Hosseinzadeh (2008) in a study argued that consumers with high nationalism
consumption(compared to consumers with low consumption nationalism) have a
better assessment of domestic goods, but closer examination showed that these
consumers evaluate the domestic goods less favorable that the foreign goods (HAGHIGHI;
HOSSEINZADEH, 2008).
Study done by
Isaac Cheah et.al. (2016) argued that customer's hostility is shown by economic
hostility and war. In such circumstances, the immense hostility and ethnicity
of customers does not play a significant role in affecting other areas in the
hostility model. But the managerial consequences such as imposing sanctions on
retailers, traders, and importers as well as launching campaigns to buy local
products will direct peoples' willingness towards domestic products (ISAAC
CHEAH, et al., 2016).
Kistruck et al. (2015)
suppose that comparative advantage of intermediation is significant under three
intertwining transaction conditions: customer heterogeneity, intermediation
risk, company learning (KISTRUCK, et al., 2015). The research results of Topçu
and Kaplan (2015) showed that consumers' ethnocentrism is negatively related to
their willingness to buy foreign products and the judgment of domestic goods
doesn't have a distinct and significant moderating effect in this regard (TOPÇU;
KAPLAN, 2015).
The research of
DaGuiso and Thio (2014) on the labels of food products states that five factors
(low price, brand, advertising by word of mouth, consumer's perception and
attitudes to product quality) affect the purchasing decision of consumers. The
relationship between price and quality is also important (DAGUISO; THIO, 2014).
Ross (2006),
believes that factors such as quality, design, features, variety, packaging
etc. are more affecting factors in the production and sales and gaining
competitive advantage (ROSS, 2006).
Jackson (2005) believes that understanding the consumer behavior is a
prerequisite to understanding how to stimulate or encourage consumer behavior (JACKSON,
2005).
Balabanis et al. (2001),
in a research showed that more consumption nationalism is related to preferring
domestic goods (BALABANIS, et al., 2001). Moon (2001), Watson and Wright (2000)
state that if there is no suitable domestic products, the nationalist consumers
will prefer products that are culturally and politically similar to their
country or to the country which they export ratherthan other countries, and
have more favorable opinions (MOON, 2001; WATSON; WRIGHT, 2000).
Similarly,
according to the explanation and background of the subject, this article has
dealt with identifying and prioritizing the factors affecting the customers'
willingness to purchase domestic goods than the foreign ones in Iran Transfo
Corporation in 2016. Because its products are as good as the foreign goods in
terms of quality, and more affordable in terms of cost and price.
However, many
customers still prefer imported goods from Italy, Russia and Poland, which
reflects a weakness in the marketing, which requires support for the domestic
goods from the government leading to economic growth and production. Preference
for domestic products will be achieved once the domestic companies compete with
foreign products through enhancing the product quality, and thinking to the
international arena, as the saying goes "the greatest defense is to
attack."
This is possible
when factors affecting customers' willingness to buy domestic and foreign goods
are identified and deficiencies and weaknesses are removed, so that besides
satisfying and attracting domestic customers, they compete in the global market
as well. Competition in the global market and more productions leads to
increased prosperity of domestic industries among both domestic and
international buyers, and all these factors require more labor in the production,
sales and so on.
2. RESEARCH PURPOSES
2.1.
main
Purposes
Identifying and
prioritizing the reasons for customers' willingness to buy domestic or foreign
goods.
2.2.
Secondary
objectives
a)
Identifying and prioritizing the performance of domestic and
foreign manufacturers according to the demands of customers.
b)
Customers' assessment of the features of domestic goods compared
to that of foreign goods.
c)
Identification of customer satisfaction with the marketing methods
of domestic goods compared to foreign goods.
d)
Identification of competitive factors, such as the similarity of
competitors and the competitive position with respect to organizational and
environmental factors.
3. THE THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK OF RESEARCH
Internationalizing
planning and business implementation, today has had a very pervasive effect on
business. Market space has become an international competitive environment for
all goods that affects business decisions in every corner of the world (DARLING;
TAYLOR, 1996).
Due to this
increase in competition, organizations have begun to present different
strategic programs (WHITE; GRIFFITH, 1997) and according to the competition
theories, creating sustainable competitive advantage is one of the primary
objectives of companies and especially marketing strategies. When the company
expands its activities in international markets, the first question that arises
is whether the company can continue its existing marketing strategies to create
sustainable competitive advantage.
Research on the
benefits and costs of marketing strategy standardization has moved in three
different directions. One stream argues in favor of standardization approach,
the second stream supports adaptation, and the third and newer stream supports
creating a conditional framework that offers a degree of standardization (VISWANATHAN;
DICKSON, 2007).
Standardization
approach is using the same marketing methods in all countries, regardless of
cultural differences. In contrast, the adaptation approach emphasized the
adaptation of marketing methods tailored to local conditions in each country (KANSO;
KITCHEN, 2004).
Debates on the standardization
against adaptation date back to 1960s. Advocators of standardization
approach refer to savings resulted from mass production, research, development
and marketing as a result of convergence in consumer tastes and globalization
of competition (BALABANIS, et al., 2001).
Experts and
advocates argue that customers vary from one country to another. Advertising
and other forms of promotion shall be dealt with tailored to the cultural needs
of the country. Therefore, executives in different countries may face with
unique obstacles such as potential differences in culture, tastes, media
infrastructure, economic development and resentment or resistance towards attempts
by companies to adjust their tastes and different cultures (KANSO; KITCHEN,
2004).
Green et al. (1975)
found that customers with different methods look at the importance of various
characteristics of the product in relation to their purchase behavior. Kanso in
1992 found that most companies conducted studies on this matter, have used
adaptation approach and the standardization perspective is diminishing.
Altogether, he
proposed that although the demands and needs of human beings are more or less the
same, but the way by which these wishes and needs are met is not the same. [Ibid.204]
Hence, international companies refine their goods and services to adapt to
customer needs. By refining goods in accordance with needs of specific market,
these companies are able to build strong customer relationships (WHITE;
GRIFFITH, 1997).
Jane (1989),
created a classification of four different factors that affect the
standardization: factors of target market, market positioning factors, factors
dependent on the nature of the goods, and organizational factors.
Colchalso noted
that instead of thinking about absolute standardization, a global marketer
should think about a degree of standardization and claimed that the desirable
level of standardization will change from a product to another. He then showed
that even if a product has all the globalization features, obviously it would
not be able to use quite the same way for advertising in the worldwide.(Kanso
& Kitchen,2004)
The highest
possible level of standardization is achieved when the
homology of customers' response to the marketing mix and the similarity
rate in economic freedom is high and competitive advantages are simply
transferable. On the other hand, at the other end of the spectrum where the
homology of customers' response to the marketing mix and the similarity rate in
economic freedom is low and competitive advantages aren't simply transferable,
standardization would be an irrational behavior in terms of competition (VISWANATHAN;
DICKSON, 2007).
By accepting the
conditional approaches of marketing approach standardization tailored to the
requirements of each market, for success in business and competition managers
should have a deep and identical understanding of the different attitudes and
expectations of customers in the markets, in which they are competing (DARLING;
TAYLOR, 1996).
The positive or
negative assessment of the customer of foreign goods can definitely have a
serious effect on different marketing decisions such as development of
appropriate segmenting and positioning strategies and moderating marketing mix
program in accordance with the customer's perceptions and modes of behavior in
different countries (LEONIDOU; et al., 2007).
According to
Fishbone in 1967, and Lancaster in 1966, customers always describe a product
with a set of its features (MATSATSINIS, et al., 2007). Customers not only buy
a product, but also a complete package of values under the title of market
proposal. This proposal contains a series of elements such goods, goods services,
transaction, brand, packaging, price, credit terms, price discounts, promotions
and marketing, personal sales, the availability of store or business, inventory
list, transportations and so on. Today, mixing and coordinating these different
elements as a proper and integrated collection is raised as the primary
challenge for Chief Marketing Officers to develop a successful competitive
position (DARLING; TAYLOR, 1996).
All research has
shown that customer orientation towards goods and marketing methods related to
it is very important in the market. Customer orientations towards various
commodities that are available from different countries can be an important
factor in determining the success of a company's marketing strategy.
The
key points that creating distinction in advantages is derived only from
goods and marketing methods that are significant to customers and the goal is
to understand the stimuli of customer satisfaction and loyalty related to his
willingness to consume and purchase specific foreign goods (WOOD, et al., 1999).
4. CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF THE RESEARCH
In this study, using
a self-made questionnaire we examine the product features (reliability,
market-product fit, product function), marketing method (reputation and
validation, relative value, communication methods) and purchase preferences are
measured and evaluated by different tests on the production of Iran Transfo
Corporation, which leads to the presentation of an objective method to develop
strategies and understand the stimuli that have greater effect on customer
purchase preferences.
According to
research from the theoretical model of Fishbone (1967) and Lancaster (1966).
Thus, according to the variables the conceptual model of the research is as
follows:
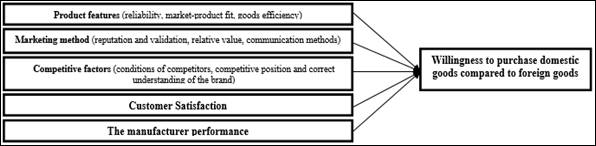
Figure1: conceptual model of the
research -Factors affecting customers ‘willingness to buy domestic products
compared to the foreign ones
5. METHODS
It's a survey
research (descriptive-correlation) carried out with two methods, namely,
library and field method and distributing questionnaires among 200 domestic and
foreign consumers of Iran Transfo Corporation and domestic companies consuming
similar foreign products. The sample was selected randomly from among all
presenters (customers) and sending electronic questionnaires.
6. QUESTIONNAIRE OF FACTORS AFFECTING THE WILLINGNESS OF
CUSTOMERS TO PURCHASE GOODS
This self-made
questionnaire includes questions such as (product features, workmanship,
quality, reliability, competitiveness, advances of technology, product
diversity, physical specifications, marketing methods, availability, after sale
services, price , etc.) that can be tested using the Likert scale. Reliability
of data using Cronbach's alpha also shows that items have an acceptable
correlation (Table 1).
Table1: Cronbach's alpha test on the variable
|
Variable
|
Number of items
|
Cronbach's alpha coefficient
|
|
Reliability
|
5
|
0.77
|
|
Market Fit
|
5
|
0.89
|
|
Product function
|
4
|
0.92
|
|
Marketing methods
|
11
|
0.85
|
|
purchase preferences
|
6
|
0.88
|
|
|
|
|
7. DATA ANALYSIS
This study is
applied in terms of purpose, and descriptive correlation in terms of data
collection. The relationship between variables is analyzed in terms of purpose,
using the SPSS software in two parts: descriptive and inferential statistics.
Finally, based on the data collected, factors affecting customers' selection
were used. In order to determine the final model and the correlation between
independent and dependent variables multiple regression method was used (Inter)
and prioritized.
8. RESULTS
8.1. Descriptive
statistics
Demographic
characteristics indicate that the 87.5% of respondents are male, and (55%) are
over 35 years and 42.5% between 25 - 34 years old. Given that the majority are
employees of large companies of power distribution. As it was expected 100% of them
have a university degree (71% BA degree, 17.5%MA degree, 6.5% Ph.D.,
4.5%Associate degree) and only 0.5% (1 person) of respondents had diploma and
lower. (Table2).
Table 2: Demographic variables
|
Percent
|
|
|
Variable
|
|
87.5
|
175
|
male
|
Sex
|
|
12.3
|
25
|
Female
|
|
2.5
|
5
|
18-24
|
Age
|
|
42.5
|
85
|
25-34
|
|
55
|
110
|
35 and above
|
|
0.5
|
1
|
Diploma or lower
|
education
|
|
4.5
|
9
|
Associate
|
|
71
|
142
|
Bachelors
|
|
17.5
|
35
|
Masters
|
|
6.5
|
13
|
Ph.D.
|
Product features
and marketing methods: the majority of respondents agreed (55.9 %) or strongly agreed
(40.9 %) that Iranian goods have reliability, and in terms of market fit, only
9.5% believed that products didn't fit with the market, and 35.5% agreed, 25.5%
strongly agreed that Iranian goods have a proper function. The majority of respondents
(36.8% agree, 31.3% strongly agree) believed that the Iranian goods have a
relative reputation and validity and 20.3% had no idea, 11% disagreed and 0.5%
strongly disagreed. The respondents also (46.5% agree and 18.5% strongly agree)
stated that the Iranian goods have relative value and more than half of
respondents (34.5 percent agree, 18.6% strongly agree) stated that Iranian
goods have an appropriate communication. Finally, most of respondents (56.5%
strongly agree, 31.2% agree) had a preference to purchase Iranian goods than
other goods. (Table 3)
Table 3. Components of the independent and the dependent variables
|
Component
|
Reliability
|
Market
Fit
|
Product
function
|
Relative
reputation and validity
|
Relative
Value
|
Modes
of communication,
|
Purchase
preferences (the dependent variable)
|
|
Freq.
|
%
|
Freq.
|
%
|
Freq.
|
%
|
Freq.
|
%
|
Freq.
|
%
|
Freq.
|
%
|
Freq.
|
%
|
|
Strongly
disagree
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0.5
|
1
|
0.5
|
7
|
3.5
|
25
|
12
|
7
|
3.5
|
|
disagree
|
0
|
0
|
19
|
9.5
|
38
|
19
|
20
|
11
|
6
|
3
|
15
|
7.7
|
0
|
0
|
|
No
idea
|
6
|
3.2
|
56
|
28
|
39
|
19.5
|
37
|
20.3
|
57
|
28.5
|
51
|
26.3
|
17
|
8.5
|
|
agree
|
102
|
55.9
|
59
|
29.5
|
71
|
35.9
|
67
|
36.8
|
93
|
46.5
|
67
|
34.5
|
62
|
31.2
|
|
strongly
agree
|
76
|
40.9
|
66
|
33
|
51
|
25.9
|
57
|
31.3
|
37
|
18.5
|
36
|
18.6
|
113
|
56.8
|
|
Missing
|
14
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
18
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
6
|
-
|
1
|
|
|
Total
|
200
|
100
|
200
|
100
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.2.
Inferential Statistics
The following
tables represent the results of the t test, mean and standard deviation of
variables towards purchasing goods from Iran Transfo Corporation and similar
companies.
Table 4: T-test table of the two
independent variables affecting the purchase preferences of domestic and
foreign goods
|
Components
|
T Value
|
The significance level (sig)
|
|
Willingness to purchase
|
4.61
|
0.000
|
|
Product features
|
0.51
|
0.611
|
|
Marketing method
|
2.18
|
0.032
|
|
Performance of manufacturers
|
1.43
|
0.153
|
|
Customer Satisfaction
|
5.81
|
0.000
|
Table 5: The mean and
standard deviation of purchasing foreign goods
|
Purchasing foreign goods
|
Component
|
|
Number
|
Mean
|
Standard
deviation
|
|
Willingness
to purchase
|
No
|
73
|
26.75
|
2.79
|
|
Yes
|
53
|
23.49
|
4.56
|
|
Product
features
|
No
|
73
|
52.71
|
11.22
|
|
Yes
|
53
|
51.75
|
9.12
|
|
Marketing
method
|
No
|
73
|
40.50
|
9.29
|
|
Yes
|
53
|
36.56
|
10.51
|
|
Performance
of manufacturers
|
No
|
73
|
93.21
|
18.68
|
|
Yes
|
53
|
88.
32
|
19.18
|
|
Customer
Satisfaction
|
No
|
73
|
8.78
|
1.26
|
|
Yes
|
53
|
7.37
|
1.38
|
Now, for better
evaluation, the results of the hypotheses in the research are presented as
follows:
·
Hypothesis 1: There is a significant difference between customers'
willingness to purchase domestic goods and foreign goods. According to the
t-test and mean tables, t = 4.61shows a significance level and the hypothesizes
confirmed because sig is less than 0.05. Therefore, there's a difference
between people who purchase domestic and foreign goods.
·
Hypothesis 2: There is a significant difference between the
customers' evaluation of the domestic and foreign product features. T = 0.51 and the
significance level equals 0.611 which shows that the t obtained is
insignificant at this level, because sig is more than 0.05and the hypothesis is
rejected.
·
Hypothesis 3: There is a significant difference between the
customers' evaluation of the marketing methods of domestic and foreign
products. T= 2.18 and the significance level equals 0.032, which shows that
the t obtained is significant at this level, because sig is less than 0.05 and
the hypothesis is confirmed. Mean table also shows the significance,
meaning that there's a significant relationship between the customers'
evaluation of the marketing methods of domestic and foreign products.
·
Hypothesis 4: There is a significant difference between the
manufacturers' performance of domestic and foreign products according to
customers' demands. T = 1.43 and the
significance level equals 0.153 which shows that the t obtained is
insignificant at this level, because sig is more than 0.05 and the hypothesis
is rejected.
·
Hypothesis 5: There is a significant difference between customer
satisfaction and willingness to purchase domestic and foreign goods. Results suggest that
T = 5.81 and the significance level equals 0.000, which shows that the t
obtained is significant at this level, and the hypothesis is confirmed.
Mean table also shows the significance, therefore there's a significant
relationship between customer satisfaction and willingness to purchase domestic
and foreign goods.
8.3. Multiple
Regressions:
Simultaneous
multiple regression method was used to determine the final model and the
correlation between independent and dependent variables (Inter), and the
interpretation of the tables are shown below:
Table 6: The final model of correlation between independent and dependent
variables
|
Model
|
R
|
The coefficient of
determination
|
Standardized coefficient
of determination
|
F
|
The significance level
(sig)
|
|
1
|
0.680
|
0.463
|
0.429
|
13.535
|
0.000
|
As seen, R equals to 0.68, which
represents a fairly good correlation between the variables. Also based on the
adjusted coefficient of determination, it can be said that 0.42percent of
changes in willingness to purchase foreign and domestic goods are explained by
7 variables. F value is significant an error-level smaller than 0.05 and it can
be concluded that the regression model of the research which is composed of 7
independent variables is a moderate model and the set of independent variables
can explain 46% of the variance of the willingness to purchase Iranian and
foreign goods.Table 7: The set of
standard and non-standard coefficients for independent and dependent variables
|
Non
standardized coefficients
|
Standardized
coefficients
|
T
|
The
significance level (sig)
|
|
|
B
|
standard
error
|
Beta
|
|
|
(Constant)
|
0.939
|
0.538
|
|
3.601
|
0.000
|
|
Reliability
|
0.079
|
0.020
|
0.364
|
3.934
|
0.000
|
|
Market Fitn
|
-0.104
|
0.020
|
-0.858
|
-5.230
|
0.000
|
|
The function of the product
|
0.052
|
0.027
|
0.416
|
1.906
|
0.059
|
|
The relative reputation
|
-0.080
|
0.015
|
-0.443
|
-5.502
|
0.000
|
|
The relative value
|
-0.066
|
0.027
|
-0.262
|
-2.423
|
0.017
|
|
communications
|
0.039
|
0.018
|
0.347
|
2.117
|
0.037
|
|
Purchase preferences
|
-0.034
|
0.014
|
-0.218
|
-2.382
|
0.019
|
The table above
shows the effect of independent variables on the dependent variable using the
coefficients B. And the beta coefficient which is the standardized regression
coefficient of each independent variable on the dependent variable, meaning
that it specifies the relative share of each independent variable in the model.
These factors suggest that the effect of 7 variables of reliability, market
fit, product performance, marketing methods that includes (relative reputation,
the relative value, and communication), and the purchase preferences are
significant at the error level less than 0.05.
Regarding the
role of each share, and the role of each affecting dimensions in the model, the
beta and its rate should be considered. According to the Table (24-4) and
regression method in the entry of variables to the final model, it can be said
that among the variables studied, the first variable that shows maximum
affectivity has market fit. In fact, it can be said that for each unit change
in the standard deviation in the market fit, it affects the purchase of
domestic goods.
The second
affecting variable is the relative reputation and validity, and it can be said
that for each one unit change in the standard deviation in relative reputation
and validity of the product, it affects the purchase of domestic products by
0.44. The third affecting variable is product function, and it can be said that
for each unit change in the standard deviation in product function, it affects
the purchase of domestic products by 0.41.
The next
effective variable is reliability of the product and it can be said that for
each unit change in the standard deviation in product reliability, it affects
purchasing domestic products by 0.36. The next affective variable is the mode
of communication and it can be said that for each unit change in the standard
deviation in the communication modes, it affects the purchase of domestic
products by 0.34. And finally it is the relative value of the product that for
each unit change in the standard deviation in the relative value of the goods,
it affects the purchase of domestic products by 0.26.
9. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
The international
market research on consumers' attitudes to domestic and foreign products and
how they make decisions for purchasing, expresses two views: First, the logical
data processing model that says consumers evaluate and select their need in a
rational process affected by the cognitive components. The second one is the emotional
model of processing information representing consumer choice affected by
emotional factors.
In choosing
between domestic and foreign goods, cognitive factors may include quality,
price, availability, after sale services and availability of spare parts for
domestic products, which leads to willingness of domestic products. So far,
most researchers consider nationalism as an important factor in purchase
preferences and many factors derived from the competitive advantage are not
mentioned.
10. THE RESULTS OF THE RESEARCH SHOWED THAT
According to
above, this study aims to identify and rank the factors affecting the
customers' willingness to purchase domestic goods rather than foreign goods in
Iran-Transfo Corporation by distributing 200 questionnaires among 26 companies,
the majority of customers 87.5% were male respondents aged 25- 35 years and
older (97.5%) with undergraduate education.
·
There is a significant difference between customers' willingness
to purchase domestic goods and foreign goods
·
There is a significant difference between the customers'
evaluation of the domestic and foreign product features.
·
There is a significant difference between the customers'
evaluation of the marketing methods of domestic and foreign products.
·
There is a significant difference between the manufacturers'
performance of domestic and foreign products according to customers' demands.
·
There is a significant difference between customer satisfaction
and willingness to purchase domestic and foreign goods.
After
prioritizing the factors affecting the purchase of domestic products, the
results of the study has stated that, firstly, the market fit variable shows
maximum effect. The second effective variable is the relative reputation and
validity of the goods.
The third
effective variable is the product function and then the product reliability,
methods of communication and finally the relative value of the goods to
purchase the goods of Iran Transfo Corporation. As a result, this research is
consistent with many domestic research, such as research done by Sadeghi, et
al. (2013), Mahmoudi Meymand, et al. (2012), Heidarzadeh, et al. (2009),
Haghighi and HosseinZadeh (2008) and foreign studies such as Isaac Cheah, et
al. (2016), Geoffrey M. Kistruck et al. (2015), Cenap T Opcu, Kaplan (2015),
Thio and Da Guiso (2014), Ross (2006), Jackson (2005).
11. SUGGESTIONS
The results
showed that products in Iran Transfo Corporation have no significant difference
foreign products in terms of product features and people prefer domestic
products rather than the foreign ones, but the
company sales don't indicate
so. After reviewing the marketing factors (in particular reputation and
validity), the results showed that the company lacks an appropriate marketing
method, and the majority people believe that the goods have a relative
reputation and validity, which was a major factor in selling failure.
Accordingly, it is suggested that:
a)
The companies adopt new policies for marketing their products.
b)
The companies send trained marketer to different provinces.
c)
Different training courses should be held in the areas of product
quality and features of the product for managers and heads of departments that
use this product.
d)
A representative or agency should be located in various provinces
to sell the product, so
that consumers
are ensured more than ever.
Given that many
foreign researchers believe that nationalism and nationalist consumer
(nationalism) has an enormous effect on selling domestic goods. Therefore, it's
required to investigate the nationalism factor on this product as well.
REFERENCE
BALABANIS, G.; DIAMANTOPOULOS, A.; MUELLER, R. D.; MELEWAR, T. C.
(2001) The impact of nationalism,
patriotism and internationalism on consumer ethnocentric tendencies. Journal of International Business Studies,
v. 32, n. 1.
DARLING, J. R.; TAYLOR, R. E. (1996) Changing attitudes of consumers towards
the products and associated marketing practices of selected European countries versus the USA, 1975-95, European Business Review, v. 96, n. 3, p.
13–22
ELECTRONIC JOURNAL BHKAM (2016). http://vista.ir/article/220617
GEOFFREY, M.; KISTRUCK, S. S.; MORRIS, J. W.; WEBB, C. E.;
STEVENSD, S. (2015) The importance of
client heterogeneity in predicting make-or-buy decisions. Journal of Operations Management, n.
33–34, p. 97–110.
HAGHIGHI, M.; HOSEINZADEH, M. (2008). Compare rates tend to use domestic goods in Tehran and other parts of
the world and explore its implications for assessment and product preferences,
journal Human Sciences Research Lecturer
in Management, Iran, v. 13, n. 4.
HEYDARZADEH, K.; HASANI PARSA, E. (2013) Effect of hedonistic values on consumer purchasing behavior, Journal of Marketing Management, n. 17,
Winter.
HEYDARZADEH, K.; MOLLAREZA NIAROJI, R. (2014) After purchasing behavior of
consumers: satisfaction or
dissatisfaction, Islamic Azad University of Qazvin.
HEYDARZADEH, K.; ZANDHESAMI, H.; HASANLO, M. M. (2010) Evaluation desire (preferences) customers
purchase decision making process of foreign goods, Journal of Marketing Management, n. 7.
ISAAC, C. H.; IAN, P.; GARICK, K.; YUAN, H. (2016) Modeling effects of consumer animosity:
Consumers' willingness to buy foreign and hybrid products, Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services,
n. 30, p. 184–192.
JACKSON, T. (2005)
Motivating
Sustainable Consumption.
Centre for Environmental Strategy, University of Surrey.
KANSO, A.; KITCHEN, P. J. (2004) Marketing consumer services internationally, Marketing Intelligence & Planning, v.
22, n. 2, p. 201-215.
KNIGH, G. A. (1999) Consumer
preferences for foreign and domestic products. Journal of Consumer Marketing, v. 16, n. 2, p.151-162.
LEONIDOU, L. C.; PALIHAWADANA, D.; TALIAS, M. A. (2007) British consumers’evaluations of US versus
Chinese goods, European Journal
of Marketing, v. 41, n. 7/8, p. 786-820
MAHMOODI MEYMAND, M.; VAZIRZANJANI, H. R.; KHALILI YADEGARI, M.
(2013) Dimensions of personality test,
the Myers-Briggs (MBTI) and the desire to buy customers, Journal of Marketing Research, n. 7, p.
165-151.
MATSATSINIS, N. F.; GRIGOROUDIS, E.; SAMARAS A. P. (2007) Comparing distributors’ judgments to buyers’
preferences, International Journal
of Retail & Distribution Management, v. 35, n. 5, p.
342-362.
MOON, B. J.; JAIN, S. C. (2001) Consumer processing of international advertising: the roles of country
of origin and consumer ethnocentrism, Journal of International Consumer Marketing, v. 14, p. 89.
ROSS, S. D.; JAMES, J. D.; VARGAS, P. (2006), Development of the scale to measure Team
brand Associations in professional sport, Journal of sport management, v. 20, n. 2.
SADEGHI, R.; KASHGAR, S.; GHASEMI, H.; KAREGAR, G. H. A. (2014) To determine the willingness of customers to
buy foreign goods from the viewpoint of manufacturers, retailers and consumers,
applied research in sport management,
v. 2, n. 2 (6 row), fall, pp. 21-32.
THU, H. A.; NGUYEN, G.; AYDA, G. (2014) Factors that influence consumer
purchasing decisions of Private Label Food Products A case study of ICA Basic.
Dissertation.
TOPÇU, U. C.; KAPLAN, M. (2015) Willingness To buy foreign products in relation to ethnocentric tendencies and world minded attitudes of consumers,
Procedia - Social and Behavioral
Sciences, n. 207, p. 157-164.
VISWANATHAN, N. K.; DICKSON, P. R. (2007) The fundamentals of standardizing global
marketing strategy, International
Marketing Review, v. 24, n. 1, p. 46-63.
WATSON J. J.; WRIGHT K. (2000) Consumer ethnocentrism and attitude toward domestic and foreign
products. European Journal of
Marketing, v. 34, n. 9/10.
WHITE, D. S.; GRIFFITH, D. A. (1997) Combining corporate and marketing strategy
for global competitiveness, Marketing
Intelligence & Planning, n. 15/4, p. 173–178.
WOOD, V. R.; DARLING, J. R.; SIDERS, M. (1999) Consumer desire to
buy and se products in international markets. International Marketing Review, v. 16,
n. 3, p. 231-256.